Efficient Solar-Based Steam & Power Generation
Harness high-temperature CSP systems with thermal storage for reliable electricity and industrial heating.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) technology uses lenses and mirrors to focus solar radiation onto a small area, generating high-temperature heat that can drive thermodynamic cycles for electricity production. Unlike traditional solar photovoltaic systems, CSP can integrate thermal energy storage, allowing electricity generation even when sunlight is unavailable—a key advantage for consistent power supply.
Key Advantages of CSP
High Efficiency
Thermodynamic cycles powered by high-temperature input achieve superior efficiency.
Energy Storage Capability
Surplus thermal energy can be stored for use during non-sunlight hours.
Optimized for High Solar Radiation Areas
Performance improves in regions with high Direct Normal Irradiation (DNI).
Challenges:
- CSP only utilizes direct sunlight, not diffuse or reflected components.
- High capital costs make it unsuitable for small-scale power generation.
Parabolic Trough Collector (PTC) Technology
Parabolic Trough Collector (PTC) Technology
Among CSP systems, parabolic trough collectors (PTC) dominate the market (~90%) due to their reliability and efficiency. PTCs focus sunlight along a line rather than a single point. Key components include:
- Parabolic Trough Reflector: Concentrates sunlight onto the receiver tube.
- Receiver Tube: Coated with high absorptance material to maximize heat absorption.
- Vacuum Insulation: The tube is encased in a vacuum to minimize heat loss. Loss of vacuum significantly increases heat loss, emphasizing the importance of proper maintenance.

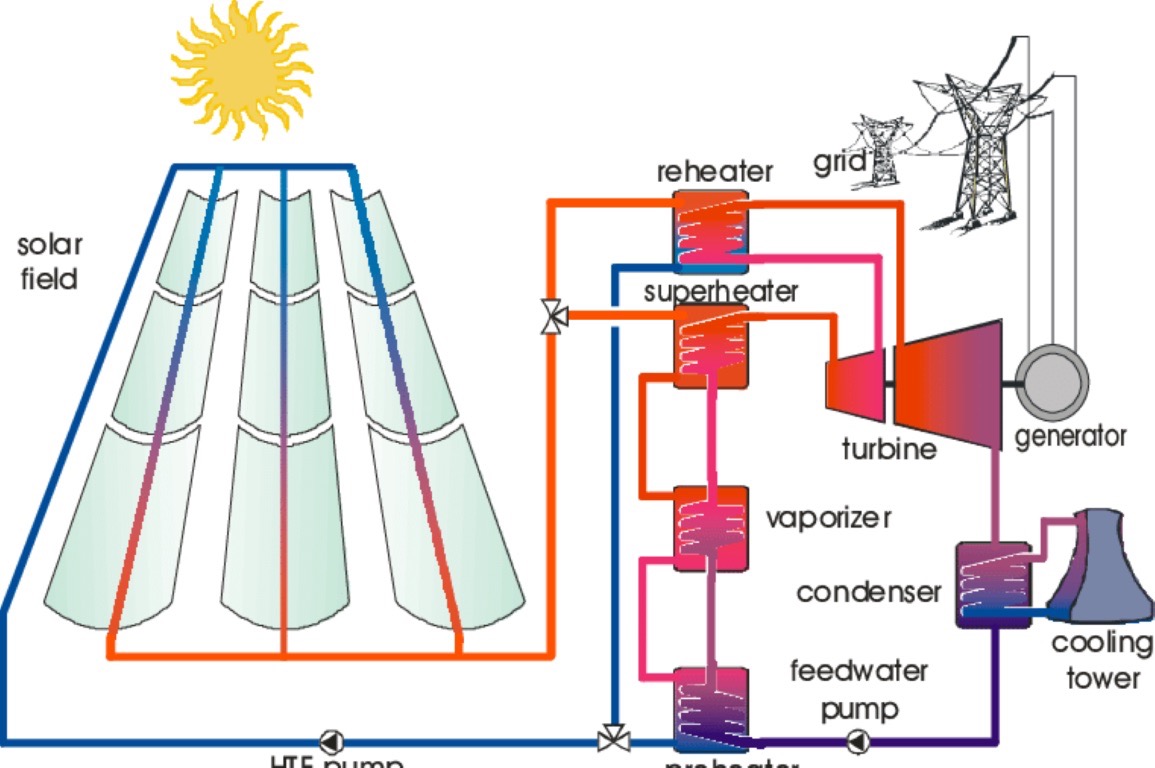
Applications
- PTCs operating at 300–400°C: Suitable for electricity generation.
- PTCs operating at 100–250°C: Used primarily for industrial heating or process heat.
Advantages of PTC Technology
- High thermal efficiency with fewer components.
- Reliable heat capture due to vacuum insulation.
- Scalable for industrial and large-scale power generation.

- – Solar Water Heating Systems
Frequently Asked Question
Need more help?
We’re here to answer any questions you may have.
What is CSP and how does it differ from solar PV?
CSP (Concentrated Solar Power) focuses sunlight to generate heat for electricity, whereas solar PV converts sunlight directly into electricity. CSP can store energy for use when sunlight isn’t available.
What are parabolic trough collectors (PTC)?
PTCs are a type of CSP system that focuses sunlight along a line to heat a receiver tube. They are efficient for electricity generation and industrial heating.
What is the working temperature range for PTC systems?
PTCs operate between 100–400°C. Lower ranges (100–250°C) are used for heating; higher ranges (300–400°C) are used for electricity generation.
Can CSP systems work at night or during cloudy days?
Yes, when integrated with thermal energy storage, CSP systems can store heat during the day and generate electricity even without sunlight.
Where are CSP systems most effective?
CSP systems perform best in regions with high Direct Normal Irradiation (DNI) and minimal cloud cover.
What maintenance is critical for PTC systems?
Ensuring the vacuum in receiver tubes remains intact, cleaning reflectors, and monitoring the heat transfer fluids are essential for efficiency and longevity.
